Security researchers have recently observed a malware distribution of Purple Fox Backdoor through trojanized installers of the Telegram messaging application.
Based on the report of Minerva Labs (https://blog.minerva-labs.com/malicious-telegram-installer-drops-purple-fox-rootkit), this threat actor was able to leave most parts of the attack under the radar by separating the attack into several small files, most of which had very low detection rates by AV engines, with the final stage leading to Purple Fox rootkit infection.
______________________________
A. Nature of Attack
The malicious Telegram installer is compiled using AutoIt with the script called “Telegram Desktop.exe”. This is only the first stage of the attack which will create a new folder named “TextInputh” and will drop a malicious downloader called TextInputh.exe.Once the malicious downloader has been executed, it will try to connect to the C&C server to download the next-stage malware. Next, the malware will check and block if there are processes associated with different antivirus before advancing to the final stage to execute the Purple Fox Rootkit.
______________________________
B. Actions to be Taken
CERT-PH recommends the following actions be taken:
- Having an anti-virus software and/or host-based detection tool running with the latest version is a must.
- Proactively monitor and secure identified systems and devices for any suspicious/malicious activities.
- Having a good backup of the system before patching is a good practice, in case there are anomalies and issues encountered.
- In addition, providing and capacitating employees with cybersecurity knowledge and information to minimize the attack surface.
- For additional information, kindly refer to the official Advisory(https://blog.minerva-labs.com/malicious-telegram-installer-drops-purple-fox-rootkit)
______________________________
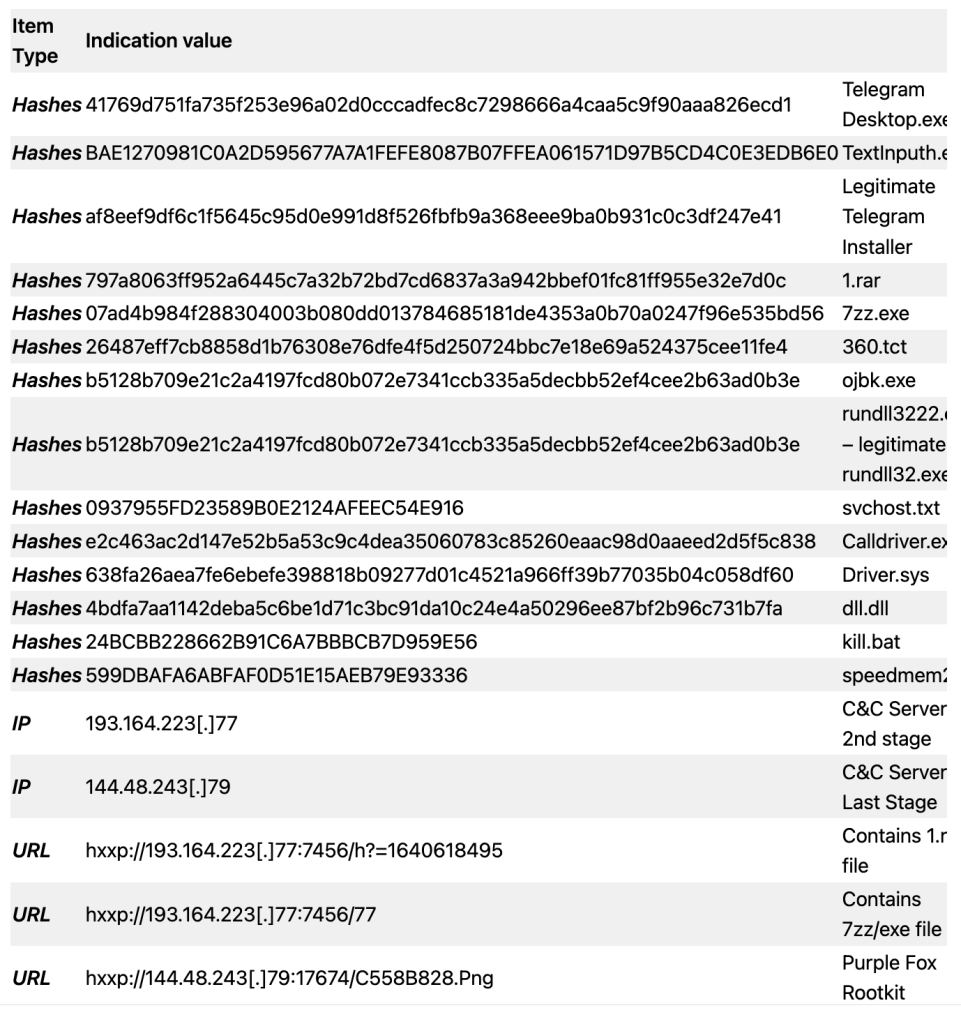
C. List of Indicators of Compromise (IOC)